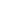
Phases
Four
BY THE
NUMBERS
28
PRODUCT FLOW
PRODUCT FLOW
· Assess Damage
· Cause & Effect Analysis
· Develop Repair Plan
· Materials
· Materials
· Equipment
· Resources
· Services (Contracts)
· Personnel
· Hardware
· Service Providers
· Repair
· Re-commission
· Restore Flow
1
2
3
4
ASSESS
PROCURE
MOBILIZE
EXECUTE
step of
Reduce the consequences of a catastrophic failure.
UNDER THE
REACTIVE
CRISIS MODEL,
operators can only respond to incidents after they occur,
which means they are often ill-prepared and ill-equipped to effectively mitigate the multifaceted
fallout. In addition to elevating safety risk and environmental impact, the reactive model results
in substantially longer downtimes and long-term damage to
reputation and shareholder value.
1
REACTIVE
CRISIS MODEL
PROACTIVE
OPERATIONAL
READINESS
2 3
BY ADOPTING THE
PROACTIVE
EPRS MODEL,
operators prepare the assessment (including
gap analysis), procurement (including long lead-time materials and equipment) and mobilization
stages of their emergency protocols prior to any incident. As a result, the operator is ideally
positioned to make safe the working area, execute cleanup and repairs, and restore production
and flow with minimal downtime.